A pharmacogenetic pilot study of CYP2C9 common genetic variant and sulfonylureas therapeutic response in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
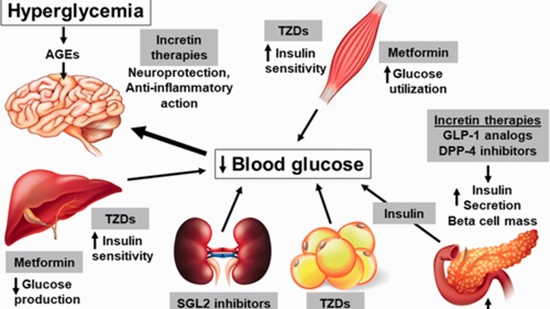
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disease that is associated with elevated blood glucose levels. Sulfonylureas (SFUs) are the most widely used among the oral antidiabetic drugs that are highly metabolized by cytochrome P450 family 2 subfamily C member 9 (CYP2C9). The CYP2C9 has been shown to be associated with a better glycemic response to SFUs and a lower treatment failure rate. The aim of the present study was to assess the influence of the CYP2C9 rs1067910 gene variant on the SFUs response in a group of Iranian patients for the first time.
Methods: Blood samples were taken from 30 patients with T2DM under sulfonylurea treatment. DNA extraction was performed using Salting out method, and then genotyping was performed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) followed by Sanger sequencing.
Results: There was no significant difference in the fasting blood sugar (FBS) between T2DM patients with different genotypes before and after the treatment with SFUs (P = 0.073 and P = 0.893, respectively). Although HbA1c was significantly different among AA, CA and CC carriers before (P = 0.001) and after (P = 0.018) treatment, no significant change was observed after treatment in all three groups.
Conclusions: In the present study based on only 30 samples in pilot survey, it is shown that the therapeutic response to SFUs was not related to rs1057910 CYP2C9 variant.
Keywords: CYP2C9 genetic variant; Pharmacogenomics; Sulfonylureas; T2DM treatment.
© Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2021.



ارسال نظر