Allele frequency of genetic variations related to the UGT1A1 gene-drug pair in a group of Iranian population
The efficacy and safety of drug treatments vary widely due to genetic variations. Pharmacogenomics investigates the impact of genetic variations on patient drug response. This research investigates the frequency of UGT1A1 genetic varia¬tions in the Iranian population, comparing them with global data to provide insights into the pharmacogenomic approach in the Iranian population.
The study was conducted using the data of the Bushehr Elderly Health (BEH) program, a population-based cohort study of the elderly population aged ≥ 60 years. Genotyping of threeUGT1A1variant alleles (UGT1A1*6,UGT1A1*27, andUGT1A1*80) was performed on a group of 2730 elderly Iranian participants with the Infinium Global Screening Array.
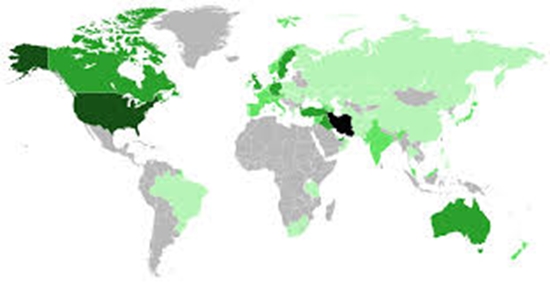
Results: The genotyping analysis revealed significant differences compared to major global populations that were addressed in the gnomAD database.UGT1A1*80 was found at a high frequency (32.34%), and followed by UGT1A1*6 (0.76%) andUGT1A1*27 (0.018) at a low frequency in the Iranian group.
Conclusions: TheUGT1A1*80 was the more prevalent allele between investigated alleles in the present study which can be considered as an important allele for pharmacogenomic testing.



comment